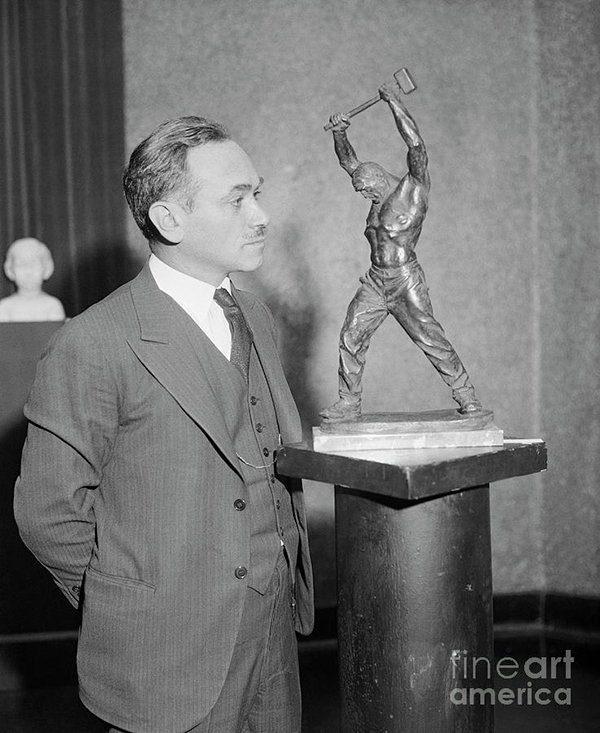
Born in Poland March 1, 1891, figurative sculptor Max Kalish came to the United States in 1894, his family settling in Ohio. A talented youth, Kalish enrolled at the Cleveland Institute of Art as a fifteen-year-old, receiving a first-place award for modeling the figure during studies with Herman Matzen. Kalish went to New York City following graduation, studying with Isidore Konti and Herbert Adams for the next two years.
Born in Poland March 1, 1891, figurative sculptor Max Kalish came to the United States in 1894, his family settling in Ohio. A talented youth, Kalish enrolled at the Cleveland Institute of Art as a fifteen-year-old, receiving a first-place award for modeling the figure during studies with Herman Matzen. Kalish went to New York City following graduation, studying with Isidore Konti and Herbert Adams for the next two years.
In 1912, Kalish studied with Paul Bartlett at the Academie Colarossi in Paris, France. In 1913, he continued his studies with Jean Antoine Injalbert at the Ecole des Beaux-Arts. The financial support of his brother, family and friends had enabled Kalish to travel to Europe. But the money ran out and, though Kalish exhibited two portrait busts in the 1913 Paris Salon, he was forced to return to America, where he worked on the Column of Progress for the 1915 Panama-Pacific Exposition, in San Francisco, California, with his former teacher, Isidore Konti.
Back in Cleveland, he worked on portrait commissions of two United States Senators and the Mayor. In the Army by 1916, Kalish sculpted a series of bronze, one-third-life-size figures of solders. In 1920, he was back in Paris, where he would begin a life-long practice of spending half the year. In 1921, he sculpted his first laborer, “The Stoker”, a genre for which he would be best known, using as a model, a Cleveland blast furnace worker. In Paris in 1922, the sculptures of laborers by Belgian artist Constantine Meunier (1831-1905) cemented Kalish’s desire to sculpt workers. Kalish won first prize for four sculptures three laborers — in 1925 at the Cleveland Artists and Craftsmen exhibition, one of which a marble nude torso was acquired by the Cleveland Museum of Art. This prize and purchase accelerated Kalish’s career. In 1928, he received a commission from the City of Cleveland for a twelve-foot-high bronze sculpture of Abraham Lincoln delivering the Gettysburg Address. It stands today in front of the west entrance of the Board of Education on East 6th Street.
Living and working in New York City in 1932, he was elected an Associate of the National Academy of Design in 1933. He later became a member of the National Sculpture Society. At the outset of World War II, Kalish was commissioned by the Museum of American History to sculpt forty-eight bronze figures — one-third-life-size — of those involved in the war effort, including President Roosevelt, his cabinet and other important people. He lived to see the work completed, though afflicted by cancer from which he died on March 18, 1945 in New York City. The sculpture of Max Kalish was included in the 1997 exhibition in Berkeley, California, “When Artists Became Workers: The People’s Art Movement of the ’30s and ’40s”, at the Judah L. Magnes Museum.
Books about the life and work of Max Kalish include Lawson Lewis’s 1933, The Sculpture of Max Kalish; the 1938 publication, Labor Sculpture by Max Kalish; James Mackay’s, 1977, Dictionary of Sculptors in Bronze; Glenn Opitz’s, 1984, Dictionary of American Sculptors; and Rediscoveries in American Sculpture by Janis Conner & Joel Rosenkranz, 1989.
Works by Max Kalish
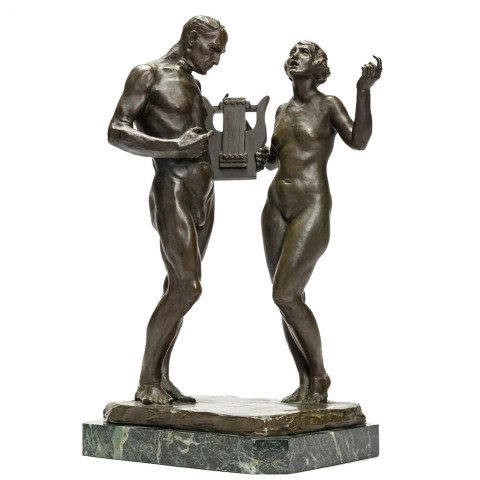

Harmony, c. 1930 Max Kalish

Nude Walking, 1930 Max Kalish

Man Power, 1930 Max Kalish

Grief Max Kalish
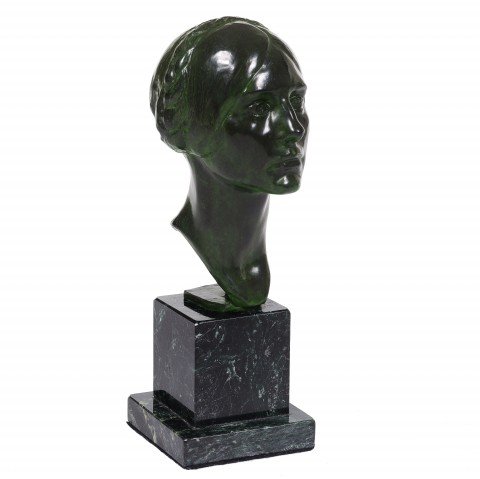

Bust of Dorothy Dietz (Wife of David Dietz), 2005 Max Kalish
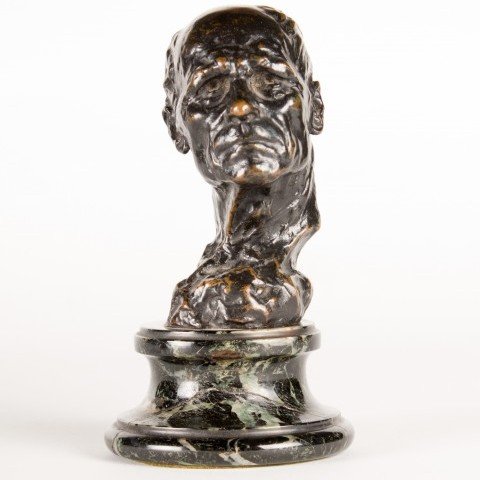

SOLD
Portrait of a Man Sculpture Max Kalish

SOLD
Road Worker, 1930 Max Kalish

SOLD
Water Carrier Max Kalish

SOLD
The Spirit of American Labor Max Kalish

SOLD
Riding a Beam, 1930 Max Kalish

SOLD
Bronze Seated Nude, 1934 Max Kalish

SOLD
The Glass Blower, 1937 Max Kalish

SOLD
Farmer Plowing, 1937 Max Kalish
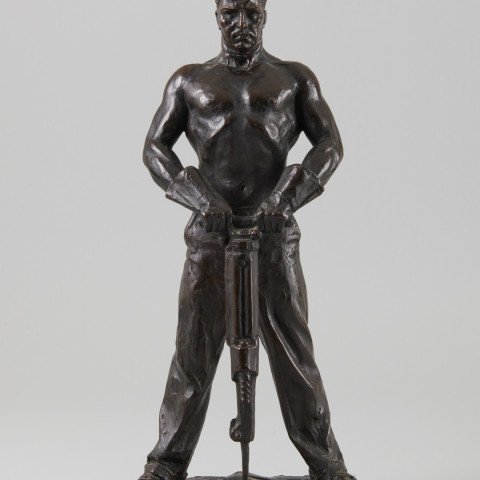

SOLD
New Power, 1937 Max Kalish